Exosomes: The Science Behind 2025's Skincare Revolution

While the world grapples with visible health crises, a stealthier threat is eroding modern medicine: antimicrobial resistance (AMR). Already responsible for over 1.2 million deaths annually, AMR could render routine infections untreatable and surgeries life-threatening within decades. This silent pandemic thrives in the shadows of antibiotic misuse, agricultural overuse, and stalled drug innovation. Here, we dissect the biological mechanisms fueling AMR, expose systemic failures in global health governance, and outline actionable strategies to avert a post-antibiotic era. The time for coordinated action—spanning policy, science, and public awareness—is now.
The beauty industry's relentless pursuit of innovation has crowned a new champion in 2025: exosomes. These microscopic extracellular vesicles, once confined to medical research, now dominate skincare conversations, promising transformative results that merge cutting-edge science with aesthetic rejuvenation. As Harper's BAZAAR declares, exosome therapy is not just a trend—it's a paradigm shift in how we approach skin health. Here's why this breakthrough is rewriting the rules of beauty.
What Are Exosomes? The Cellular Courier System
Exosomes are tiny lipid-bound vesicles (30–150 nanometers in diameter) secreted by cells to facilitate intercellular communication. They act as biological messengers, transporting proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids to target cells, regulating processes like tissue repair and inflammation. Their discovery, rooted in Nobel Prize-winning research on cellular transport mechanisms in 2013, laid the groundwork for their medical and cosmetic applications. Unlike traditional skincare ingredients, exosomes work at a cellular level, mimicking the body's natural repair systems to address aging, damage, and inflammation.
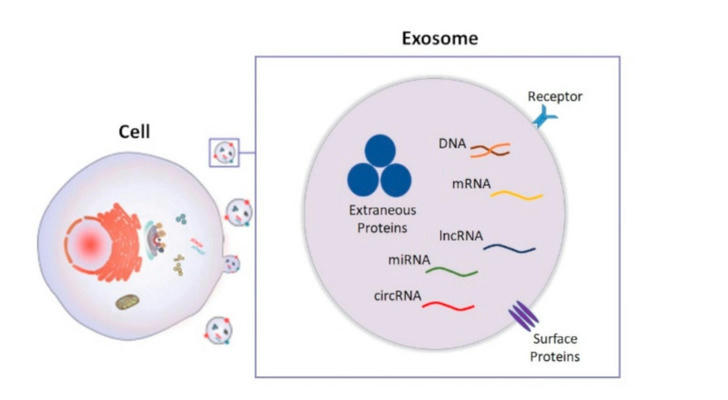
Practical Insight: For consumers, this means exosome-based products can bypass surface-level treatments by delivering bioactive molecules directly to skin cells, enhancing efficacy compared to conventional serums or creams.
The Skincare Mechanism: How Exosomes Rejuvenate Skin
Collagen Synthesis and Elasticity Restoration
Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) stimulate fibroblasts—the cells responsible for producing collagen and elastin. Studies show that human umbilical cord-derived MSC exosomes enhance collagen synthesis by up to 300%, effectively reducing wrinkles and improving skin firmness. For example, a 2023 Nature Communications study demonstrated that topical exosome application increased skin thickness in aged mice by 25%. This makes them a potent alternative to invasive procedures like laser therapy.
Implementation Tip: Clinics often combine exosomes with microneedling or fractional lasers to enhance penetration into the dermis, where collagen regeneration occurs.
Anti-Inflammatory and Repair Properties
Chronic inflammation underlies conditions like acne, rosacea, and sensitivity. Exosomes modulate immune responses by suppressing pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-1α) while promoting tissue regeneration. For instance, MSC exosomes accelerate wound healing by upregulating growth factors like VEGF and FGF, which repair damaged capillaries and restore skin barrier function. A 2024 clinical trial published in Scientific Reports found that exosome-treated wounds healed 2.1 times faster than controls.
Clinical Application: Dermatologists recommend exosome-infused serums post-procedural treatments (e.g., chemical peels) to reduce redness and downtime.
Combating Oxidative Stress
Aging skin accumulates reactive oxygen species (ROS), leading to cellular damage. Exosomes counteract this by delivering antioxidants and enzymes that neutralize free radicals. Research demonstrates that exosome-treated skin exhibits reduced oxidative markers, resulting in a brighter, more even complexion. For example, plant-derived exosomes from grapes or aloe vera are being explored for their sustainable antioxidant properties.
Exosome Applications in Modern Aesthetics
Targeted Solutions for Complex Concerns
Sensitive Skin Repair: Exosomes enriched with KGF and FGF thicken the dermis, reducing redness and strengthening fragile skin barriers. A 2025 study by Huazhong University of Science and Technology showed a 37% improvement in barrier function after 12 weeks of treatment.
Acne and Scar Mitigation: By delivering EGF and PDGF, exosomes accelerate tissue remodeling, minimizing post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation and smoothing textural irregularities.
Hair Regeneration: MSC exosomes reactivate dormant hair follicles by stimulating dermal papilla cells, offering hope for androgenetic alopecia.
Synergy with Advanced Treatments
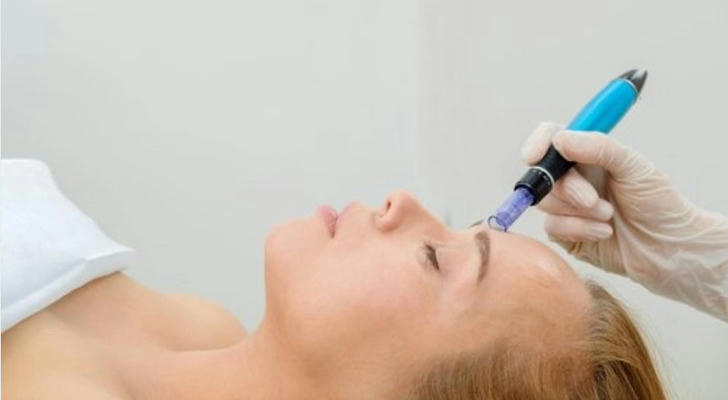
Clinicians increasingly pair exosomes with microneedling, PRP (platelet-rich plasma), or laser resurfacing. These combinations enhance exosome penetration into deeper skin layers, amplifying collagen production and reducing downtime. For instance, post-laser exosome application can shorten recovery by 40% while improving outcomes.
Step-by-Step Protocol:
Pre-Treatment: Cleanse skin and apply a numbing cream if using microneedling.
Procedure: Use a dermapen (0.5–1.5 mm depth) to create microchannels.
Exosome Application: Apply a concentrated exosome serum immediately post-procedure.
Aftercare: Use a hydrating mask and avoid sun exposure for 48 hours.
Exosomes vs. Traditional Skincare: A Scientific Edge
While retinoids and peptides remain staples, their efficacy is limited by molecular size and stability. Exosomes, however, bypass these hurdles:
Bioavailability: Their nano-scale structure allows effortless absorption into the epidermis and dermis.
Multifunctionality: A single exosome formulation can address multiple concerns—hydration, elasticity, and pigmentation—simultaneously.
Safety: As natural cell derivatives, exosomes minimize irritation risks compared to synthetic actives like AHAs or retinols.
Consumer Guidance: Look for products labeled "MSC-derived exosomes" or "plant exosomes," and ensure third-party testing for purity and concentration.
The Future of Exosome-Based Beauty
The next frontier involves personalized exosome therapies, where vesicles are tailored to individual genetic profiles or specific skin conditions. Researchers are also exploring plant-derived exosomes (e.g., from grapes or aloe) for sustainable, vegan-friendly options. However, challenges remain, including standardization of production and long-term safety data. Regulatory bodies are now developing guidelines to ensure quality control, as the market surges toward a projected $500 million valuation by 2026.
Innovation Spotlight:
AI-Driven Formulations: Companies like Dior are integrating AI skin analysis with 3D bioprinting to create custom exosome serums.
At-Home Devices: Emerging handheld devices with nano-needle arrays aim to deliver exosomes effectively without clinical visits.
Conclusion
Exosomes represent a fusion of biology and beauty, offering solutions that are as intelligent as they are effective. By harnessing the body's innate repair mechanisms, they redefine anti-aging and therapeutic skincare. As science continues to unravel their potential, one truth is clear: the future of beauty lies not in masking flaws but in empowering the skin to heal itself.
